The Rising Popularity of Earning a Degree Online
The internet opened up a world of learning possibilities, and with it came a deviation from traditional education to online learning. Data shows that online education has steadily gained popularity over the last 20 years.
In 2018, almost seven million students enrolled in distance education courses, according to the National Center for Education Statistics. That means more than one-third of all U.S. college students took at least one online class.
Globally, the online learning industry reached $200 billion in 2019, and with the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic, it is projected to hit $375 billion by 2026.
Technological advancements, increased accessibility, and the need for a work-life balance are among the reasons why more students are choosing to earn a degree online.
The Rise of Distance Education
In 2006, Congress eliminated a restriction from the Higher Education Act that prevented colleges and universities from offering more than 50% of their classes online. Since then, data has shown an increase in online degree enrollment year-over-year.
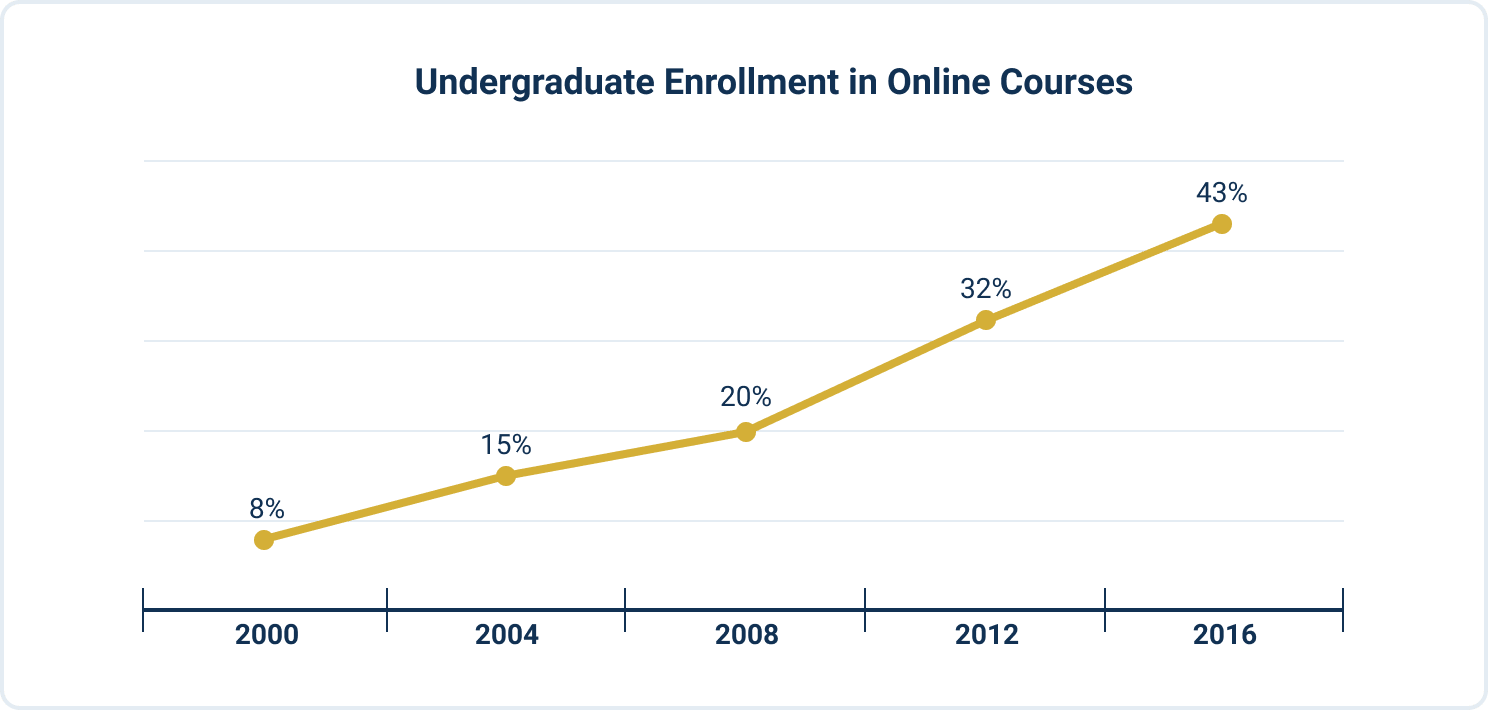
In 2000, undergraduate enrollment in online courses was eight percent. It jumped to 20% in 2008 and increased to 32% in 2012. By the 2015-2016 school year, at least 43% of undergraduate students took at least one online class.
Fast forward to 2018-2019, where 79% of colleges offered distance education courses or entire degree programs online. That translated to almost every public four- and two-year college offering a distance education course or program.
These expanded offerings contributed to the upward trend of students earning degrees online. While distance education gained traction, traditional colleges saw a decline in student enrollment.
Traditional Education vs. Online Education
Throughout the past decade, enrollment in online courses has outpaced enrollment at traditional colleges.
From 2000 to 2010, total undergraduate enrollment in degree-granting postsecondary institutions increased 37% from 13.2 to 18.1 million students. But then, from 2010 to 2018, it decreased 8% from 18.1 to 16.6 million students, according to the National Center for Education Statistics.
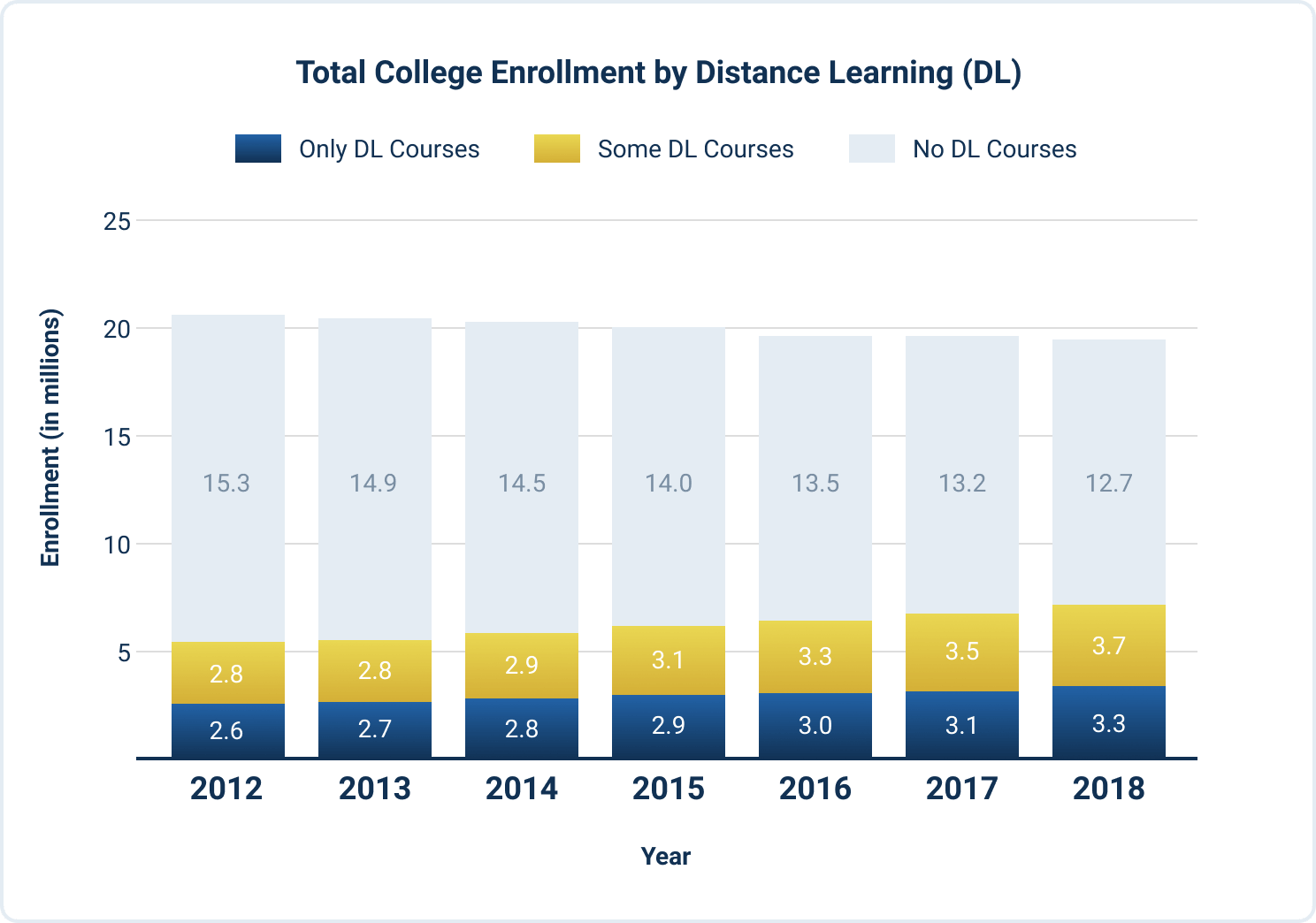
Despite the decline of overall college enrollment during this time period, the number of undergraduate students enrolled in online courses steadily increased. From Fall 2012 to 2018, distance education course enrollment increased 29%, from 5.4 to 6.9 million.
Some students juggled a combination of in-person learning with distance learning, while others completed their entire degree program exclusively online.
Between Fall 2012 and 2018, the number of students enrolled in a combination of face-to-face and distance learning courses increased 33%, from 2.8 to 3.7 million. Students enrolled exclusively in distance education courses grew 24%, from 2.6 to 3.3. million.
Online Master's Courses vs. Undergraduate
Data shows distance education to be a popular choice among master's degree students.
In 2018, the National Center for Education Statistics reported:

Post-baccalaureate students enrolled in distance learning courses; 30.7% were online exclusively, while 9% took some online classes.

Undergraduate students enrolled in distance learning courses; 14% were online exclusively, while 20.5% took some online classes.
Tuition cost could be a significant driving force as to why more master's students choose to earn degrees online. From 1996 to 2016, the average price of tuition and fees for master's degree students increased 79% compared to a 47% increase for full-time bachelor's students.
Why Some Students Prefer Distance Learning
Students pursue online degrees over traditional education for a multitude of reasons. However, the most common themes seem to be affordability, flexibility, accessibility, and career goals.
Affordability
In a 2020-2021 report, the College Board estimated the annual tuition rate to attend a four-year public college to be $27,020. In comparison, the most affordable online colleges offer degrees with annual tuition rates of $10,000 or less.
In general, distance learning is cheaper than attending a traditional brick and mortar college due to the lower overhead costs and elimination of additional expenses like transportation, room and board, course materials, and meal plans. As a result, students may take out smaller student loans, if any.
In early 2020, more than half of students cited affordability as the primary factor for their decision to enroll in distance learning.
Flexibility
Online education allows students to tailor coursework around a personal schedule. This level of flexibility is a huge draw for parents, caregivers, adults seeking career opportunities, or people working full-time.
Most online college students at both the undergraduate (51%) and graduate (70%) level are employed full-time, and 41% of all online students are parents.
Furthermore, the study showed that more than three in five students (63%) chose to study online because it worked best for their work/life responsibilities. It's evident that convenience plays a significant role in distance learning, so much so that one-third of students admitted that they would pay higher tuition for a program that offers more convenience.
Career Change and Skill Upgrade
The flexibility and accessibility of distance education allow more adults to balance an online degree program while working full-time.
A (pre-pandemic) 2020 report discovered that most students seeking online degrees did it for career-oriented reasons. It found:

Wanted to start a new career with a higher income

Wanted to start a new career more aligned with their interests

Wanted to get a promotion within their present profession
The Impact of COVID-19 on Distance Learning
The Covid-19 pandemic dramatically disrupted education in the U.S. Most colleges and universities abruptly closed their campuses and transitioned to distance learning. Many were unprepared to go fully remote and hit hurdles along the way.
By Fall 2020, some colleges were primarily online or in-person, while others chose a hybrid model. Only 4% of colleges resumed fully in-person instruction. Unsurprisingly, considering the shift in instruction format and the general air of uncertainty during that time, overall enrollment declined -2.5 %. First-time student enrollment was down -13.1%, and public two-year institutions saw a -10% drop from Fall 2019.
The downward trend in higher education enrollment partially continued into Spring 2021. Undergraduate enrollment declined -4.5%; however, graduate enrollment increased 4.3%. Additionally, both Fall 2020 and Spring 2021 enrollment increased 7% at primarily online institutions.
While it seems Covid-19 may have stalled distance learning's upward trajectory, it also forced many colleges and universities to install a remote learning infrastructure. Most have continued instruction in a hybrid or partially online format, and others are still evaluating the future of online programs.
One silver lining? The pandemic's forced shift to distance learning pushed virtual education mainstream and normalized it in a way that could alter the educational landscape permanently.
Are Online Degrees Respected by Employers?
A general concern among students is if an employer will take an online degree seriously since it didn't come from a traditional classroom setting.
Recent data shows an increasing acceptance among HR leaders. More than 60% perceive online credentials to be equal to those earned in-person.
More than 60% of HR leaders perceive online credentials to be equal to those earned in-person.
Another factor employers may consider is accreditation. Accreditation verifies educational programs meet quality standards. According to the U.S. Secretary of Education, "accreditation of an institution or program by a recognized accrediting agency provides a reasonable assurance of quality and acceptance by employers of diplomas and degrees."
On the other hand, non-accredited degree programs might make an employer suspicious, but overall, they're likely more concerned with qualifications. At the end of the day, traditional and online degrees are the exact same degrees, and many employers can't tell the difference on a resume unless specified.
Overall, the stigmas that once surrounded online degrees seem to be fading as the appeal of and acceptance toward distance education continues to grow.
Related Articles
2023 Best Online Community Colleges
Explore the best community colleges in the country that offer online degrees in 2023 and learn more about whether community college might be right for you.
By OnlineU Staff Writers | 1/10/2023
